OVERVIEW
AN OBJET D’ART HONOURING THE CRAFT SKILLS OF LA GRANDE MAISON’S MÉTIERS RARES® ATELIER
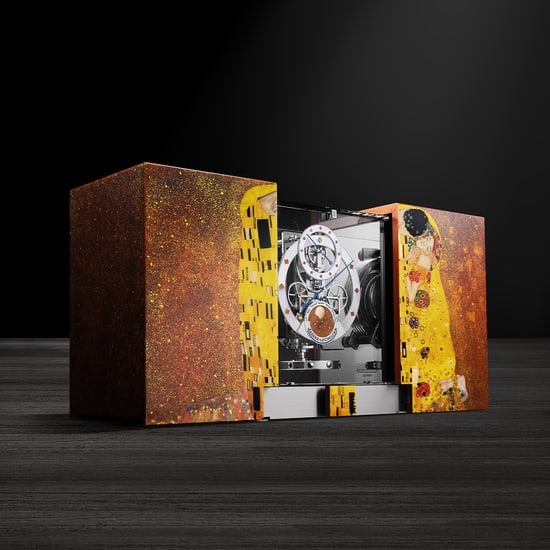
Noble in presence and delicate in detail, the Atmos Régulateur ‘Cherry Blossom’ is a one-of-a-kind work of art, showcasing the clock’s mechanism within a transparent glass cabinet set between two dramatic panels of black Grand Feu enamel. A branch of cherry blossom, hand-painted in enamel, extends seamlessly from one side, across the dial ring, to the opposite panel. Petals scatter in the air around it, as if shaken free by a passing breeze.




DESIGN
SAKURA CELEBRATING HUMAN CREATIVITY
With the enamelling alone requiring 200 hours of dedicated work by the master artisans in the Métiers Rares® atelier of Jaeger-LeCoultre, this is the largest enamelled piece ever undertaken at La Grande Maison. While the enamellers have thoroughly mastered the techniques of enamelling on watch cases and dials, the large scale of this piece presented an entirely different set of challenges. Rising to it, the artisans of the atelier worked closely together, spending countless hours on preliminary research, exchanging ideas, experimenting and making trials before the enamelling could begin in earnest. Materials and techniques were examined and reconsidered – and a new kiln specified, to accommodate such large pieces.
A one-of-a-kind work of art, the Atmos Régulateur ‘Cherry Blossom’ is the largest piece ever created in Grand Feu enamel by Jaeger-LeCoultre, requiring 200 hours for the enamelling work alone.
THE PANELS
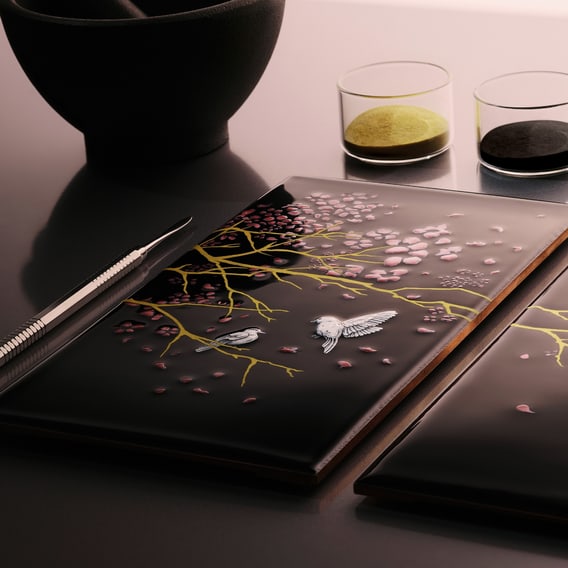
For the panels – measuring 196mm by 105.2mm – copper was found to be more suitable than the gold used for enamelling on watches. For such large surfaces, the enamellers had to perfect the ‘dry enamelling’ technique of sifting powdered pigment onto the copper plates (rather like dusting the top of a cake with icing sugar), repeating the process again and again, to achieve the desired depth and uniformity of black. After every layer, the panels had to be fired, then cooled and perfectly flattened – with every stage carrying the risk of bubbling, cracking or dust specks, any of which would ruin the work.

THE DIALS
For the two dial rings, it was determined that silver was the best material – despite its being a soft metal and therefore less resistant to firing at the high temperatures required for grand feu enamel. Normally, to prevent deformation, the back of an object is prepared with ‘contre-email’, but in this case it was impossible since the dial is visible from behind. The rings were hollowed out to form a trough into which the enamel was applied. Then, as for the panels, came the challenge of multiple firings.
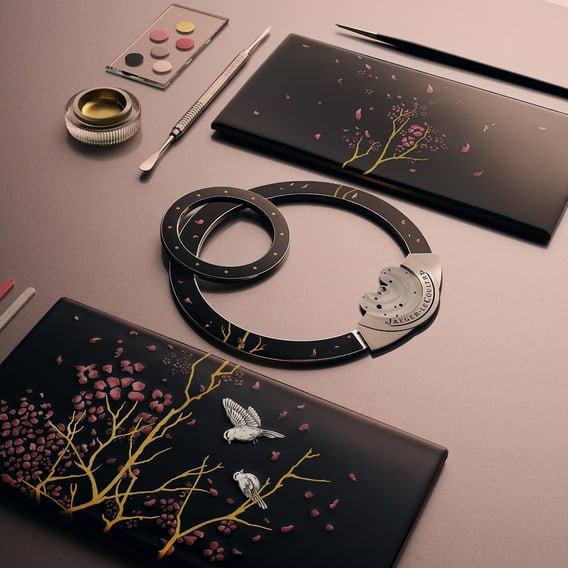

MINIATURE ENAMELLING
Finally, when the black enamel backgrounds were completed to perfection, the work of the miniature-painter could begin – bringing with it the almost contradictory needs for artistic flair and absolute precision. As with the black enamel, this work was done in a series of layers, each needing to be fired, with every firing again carrying the risk of damaging everything that had been done before. To succeed in such work is testament to an extraordinary level of finesse, and a degree of mastery that can be achieved only with countless years of experience.

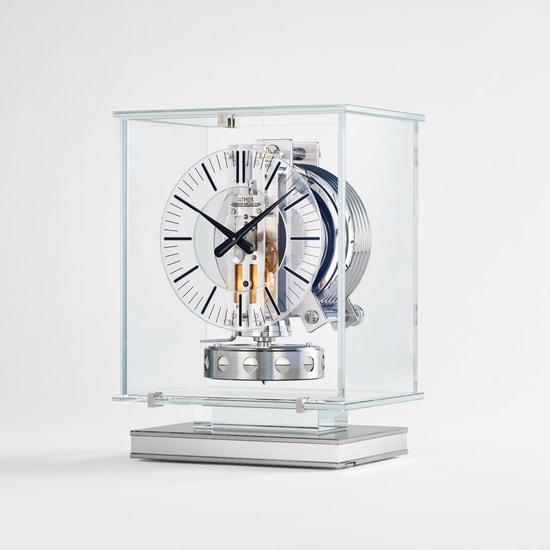
Heritage
A revolution in timekeeping
Thanks to a revolutionary mechanism invented by Jean-Léon Reutter in 1928 and brought to market by Jaeger-LeCoultre in the 1930s, the Atmos luxury clock lives on air. Its superb design has been reinvented and recrafted since its creation, elevating it to the rank of icon. Nicknamed the “President’s Clock”, the Atmos was the official gift of the Swiss Confederation.


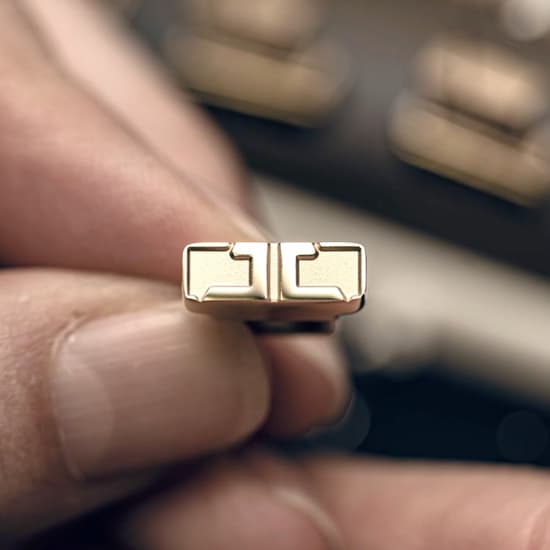
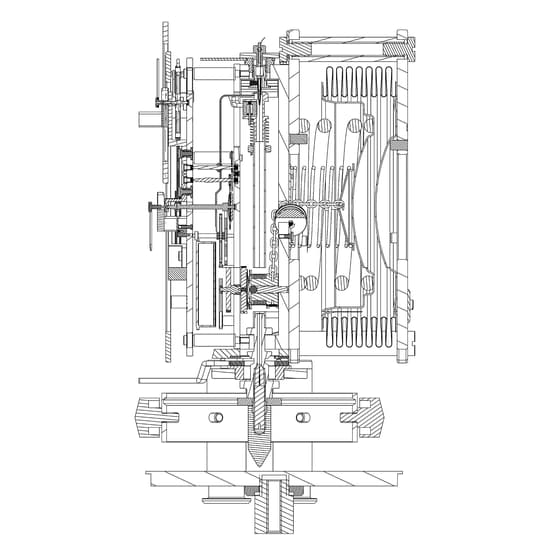
CALIBRE
PERPETUAL TIME
The movement of this exceptional piece, conceived and entirely produced within La Grande Maison, is the Jaeger-LeCoultre Calibre 582, which is distinguished by its regulator display. With an architecture defined by circles within circles, the large minutes ring and smaller hours ring are complemented by a monthly calendar and moon-phase display, as well as by the shape of the annular balance that slowly oscillates beneath the displays. The moon-phase indication is so precise that it will take 3,821 years to diverge by just one day from astronomical reality.


What's next?
The story continues